[JavaScript] string, Array 관련함수 연습
in JavaScript on Study
1️⃣ 목표
- string자료형과 array(배열)관련 함수에 대해 복습
2️⃣ String 다루기
(1) split()
- 구분자를 인자로 받아 문자를 구분한 것을 배열로 만들어 반환합니다.
const animals = "monkey, hen, dog";
const result1 = fruits.split();
const result2 = fruits.split(", ");
["monkey, hen, dog"]
(3) ["monkey", "hen", "dog"]
3️⃣ Array 다루기
(1) join()
- (array)배열의 모든 요소를 연결해 하나의 문자열로 만들어 반환합니다.
- 기본적으로
,을 구분자로 사용하며 문자열을 인자로 받아 구분자로 사용이 가능합니다.
const animals = ["monkey", "hen", "dog"];
const result1 = animals.join();
const result2 = animals.join(" & ");
monkey,hen,dog
monkey & hen & dog
(2) reverse()
- (array)배열의 요소를 역순</rd>으로 바꿔줍니다.
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
array.reverse();
(5) [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
(3) Object.assign()
- 첫번째 인자(배열)에 두번째 인자(배열)의 요소를 복사해서 넣어줍니다.
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const array2 = [];
Object.assign(array2, array);
(5) [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
(5) [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
(4) 배열자르기
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
- 위와같은 배열에서 앞의
2개원소를 제거 하는 방법을 다음과 같이 3가지 방법로 해결해 보겠습니다.
{
/* shift() */
function solution1() {
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
array.shift();
array.shift();
console.log(array); // [3, 4, 5]
}
/* slice() */
function solution2() {
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const result = array.slice(2);
console.log(array); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
console.log(result); // [3, 4, 5]
}
/* splice() */
function solution3() {
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const result = array.splice(2, 3, "a");
console.log(array); // [1, 2, a]
console.log(result); // [3, 4, 5]
}
solution1();
solution2();
solution3();
}
- solution1:
shift()를 이용하면 배열의 요소를 앞부분부터 한개씩 빼줍니다. (원본배열을 변경) - solution2:
slice()를 이용하면 인자수만큼 요소를 제거한 배열을 반환합니다. (원본배열은 보존) - solution3:
splice()를 이용하면 첫번째, 두번째인자를 이용하여 제거할 요소의 범위를 잡을 수 있고 그 이후 순번의 인자를 제거된 요소위치에 순차적으로 채워줍니다.
3️⃣ Object요소 다루기(배열관련 함수이용)
- 이번에는 다음과 같이 class(개체)를 만들어서 다뤄보도록하겠습니다.
animals라는 배열에 각각의 인스턴스들을 요소로 사용하기 때문에 결론적으로 배열관련 메소드를 이용하여 다뤄볼 계획입니다.
class Animal {
constructor(species, name, age, canSwim) {
this.species = species;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.canSwim = canSwim;
}
}
const animals = [
new Animal("🐒", "kiki", 3, false),
new Animal("🐬", "allie", 4, true),
new Animal("🐓", "kkokko", 1, false),
new Animal("🦭", "ping", 7, true),
new Animal("🐠", "lala", 1, true),
];
(1) find(), filter()
find()를 사용하면 true를 반환 하는 첫 번재요소를 찾아 반환합니다.
const result = animals.find((animal) => animal.age === 1);
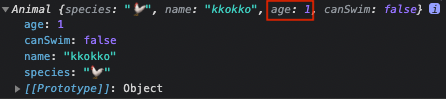
- 하지만 위의
animals배열을 보면age === 1인 요소는 2개입니다.filter()를 이용하면 조건에 맞는(true를 반환)하는 모든 요소를 포함하는 배열을 만들어 반환합니다. (원본배열을 보존)
const result = animals.filter((animal) => animal.age === 1);
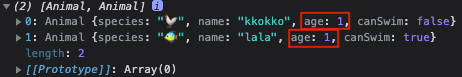
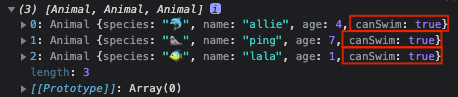
- 이번엔 수영이 가능(canSwim)한 동물들만
필터링 해봤습니다.
const result = animals.filter((animal) => animal.canSwim === true);
(2) map()
- 이번에는 animals배열의 각각의 인스턴스들을 새로운 요소로 치환하여 새로운 배열로 만들어 주기위해
map()함수를 이용하겠습니다. (원본배열은 보존)
const result = animals.map((animal) => animal.species);
- 각각의 Animal 인스턴스의 species🐒요소만 추출하여 새로운 배열로 만들어줬습니다.
(3) some(), every()
- 채크해주는 함수 입니다. 하나의 인스턴스라도 조건에 맞으면(true반환)하면 true를 반환합니다.
const result = animals.some((animal) => animal.age > 7); // false
const result = animals.some((animal) => animal.age < 3); // true
- 위의 코드에서 7살이상 동물이 없으므로 false를 반환한 모습을 볼 수 있습니다.
some()함수와 비슷함수로every()함수가 있습니다.every()함수는 모든 인스턴스가 조건에 맞아야(true반환) true를 반환합니다.
const result = animals.every((animal) => animal.age < 8); // true
const result2 = animals.every((animal) => animal.canSwin == true); // false
(4) reduce()
reduce()함수도 배열의 요소를 순차적으로 탐색하여 진행합니다.- 매개변수로 누적된값( accumulated number)과 요소를 받는 함수를 “첫번째 인자”로 대입합니다. (‘누적된 값’자리에 이전번 요소에 호출된 함수의 반환값이 대입됩니다.)
- 대입한 함수의 누적된값( accumulated number)의 초기값을 “두번째 인자”로 대입합니다. (가장 첫 순번에는
누적된 값을 얻어올 수 없으므로 직접지정하기 위함)
const result = animals.reduce((accum, animal) => accum + animal.age, 0);
- 위의 코드는
reduce()를 이용하여 모든 요소의 나이(age)의 합을 구하는 코드입니다.
